[Notes & HW Answers] 6.2 Constructing Antiderivatives Analytically.pdf
0.93MB


[Prepwork 6.2]
Q1. If 𝐹(𝑥) is an antiderivative of 𝑓(𝑥), what is the most general antiderivative?
A: The most general antiderivative = F(x) + C
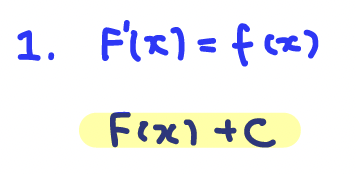
Q2. Using the properties of antiderivatives in theorem 6.1 to find
∫(3cos(𝑥)+2sin(𝑥))𝑑𝑥
A: ∫(3cos(𝑥)+2sin(𝑥))𝑑𝑥= 3sin(x) - 2cos(x) + C

Q3. Use the Fundamental Theorem to calculate the following integral exactly:
A: ∫^(𝜋/3)_0 (2/cos^2𝜃) 𝑑𝜃= 2tan(𝜋/3) - 2tan(0)
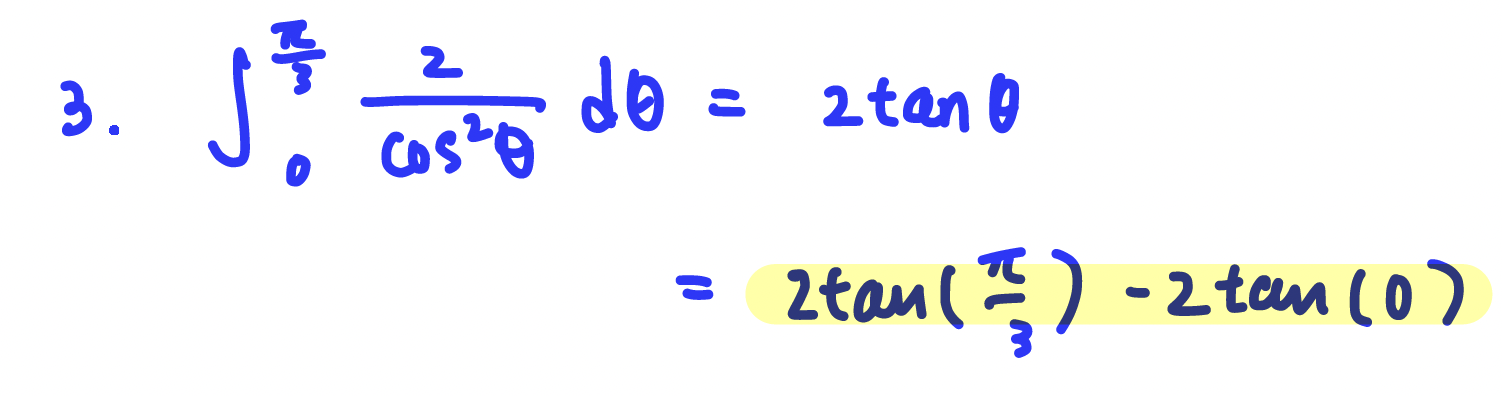
[HW 6.2]
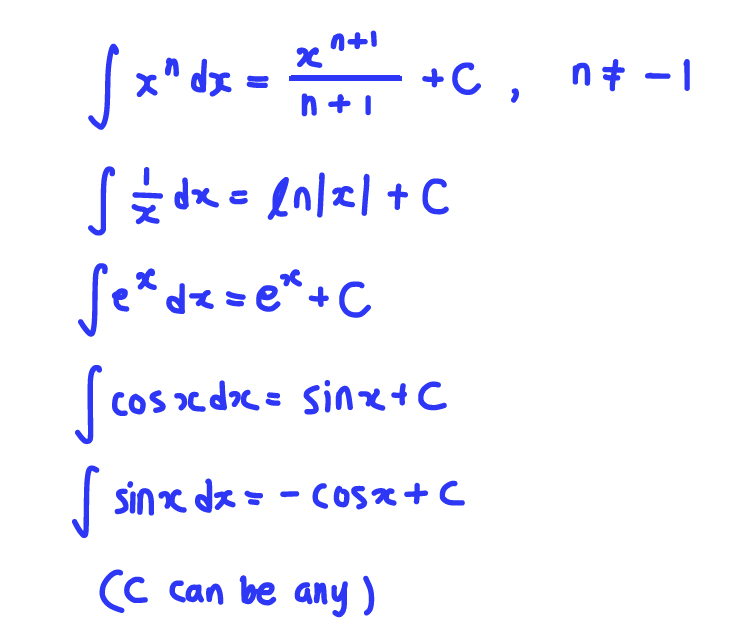
Q1. Find an antiderivative 𝐺 of 𝑔(𝑧)=1/𝑧^6
A: 𝐺(𝑧)= (-1/5)z^(-5)+1
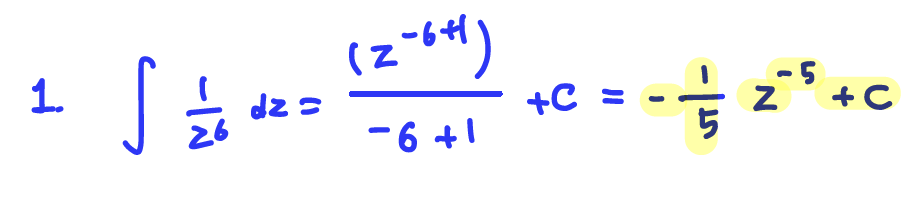
Q2. Find an antiderivative 𝑃 of 𝑝(𝑠)=3sin(3𝑠).
A: 𝑝(𝑠)= -cos(3s)+3
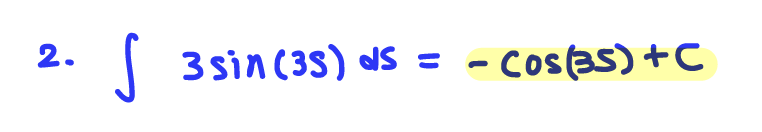
Q3. Find an antiderivative 𝐹(𝑥) of 𝑓(𝑥)=3𝑥−(x)^(1/2).
A: 𝐹(𝑥)= (3/2)x^2-(2/3)x^(3/2)+1
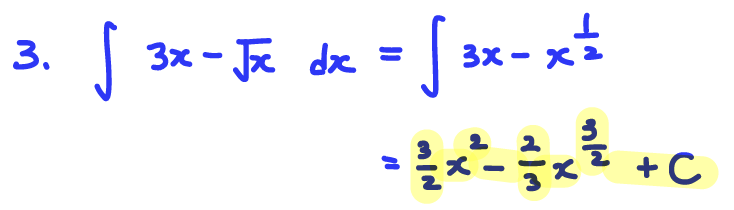
Q4. Find an antiderivative𝑃 of 𝑝(𝑡)=1 / (t)^(1/2).
A: 𝑃(𝑡)= 2t^(1/2)+3
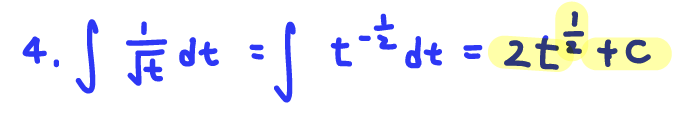
Q5. Evaluate exactly, using the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus:
A: ∫^𝑟_0 2𝑒^𝑥 𝑑𝑥= 2e^r-2
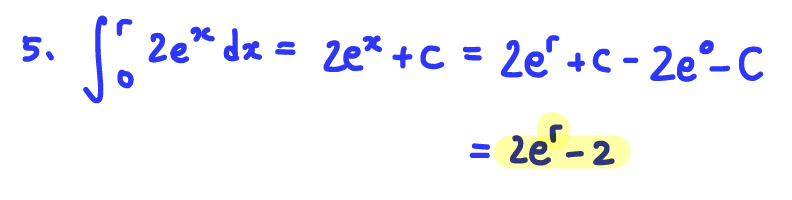
Q6. Evaluate exactly, using the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus:
A: ∫^𝑟_0 (𝑥^6/7+2𝑥) 𝑑𝑥= r^7/49+r^2
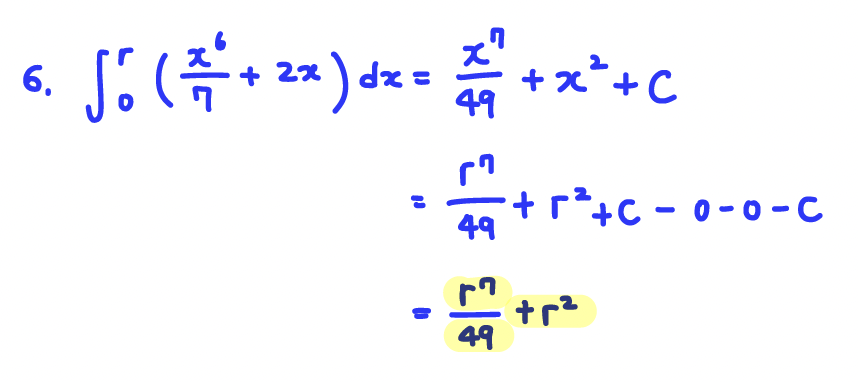
'[Umich] COE Core > MATH 115 (Calc 1)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Calculus 1 Summary Notes (0) | 2022.12.13 |
|---|---|
| [Notes & HW Answers] 6.1 Antiderivatives Graphically and Numerically (0) | 2022.12.08 |
| [Notes & HW Answers] 5.4 Theorems about Definite Integral (0) | 2022.12.06 |
| [Notes & HW Answers] 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (0) | 2022.12.06 |
| [Notes & HW Answers] 5.2 The Definite Integral (0) | 2022.12.06 |




댓글